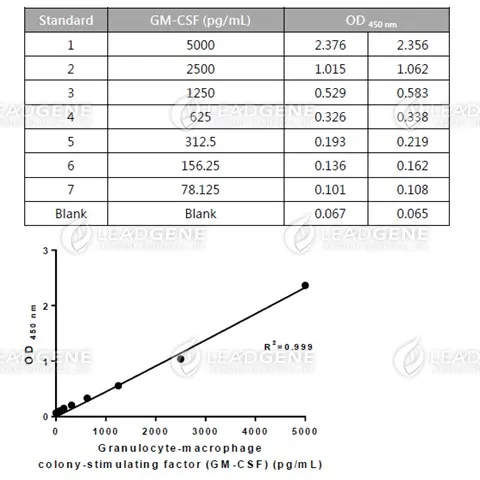
Description
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) was first identified as a Growth Factors due to its ability to induce proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow progenitors into granulocytes and macrophages. GM-CSF is produced by multiple cell types including activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, endothelial cells and fibroblasts upon receiving immune stimuli. GM-CSF stimulates stem cells to produce granulocytes and monocytes functions as a cytokine.
Test Principle
Human GM-CSF ELISA kit is used to detect GM-CSF in samples by sandwich ELISA method. This assay uses microplate pre-coated with mouse anti-human GM-CSF monoclonal antibody to the solid phase. Human GM-CSF in the sample conjugates on solid phase and then react with the HRP conjugated mouse anti-human GM-CSF monoclonal antibody. Subsequent wash steps will remove residual unbound antibody. After incubation with substrate solution, the reaction is determined by the absorbance at 450 nm. Quantification of nuclease level is accomplished by comparing the absorbance with standard curve.