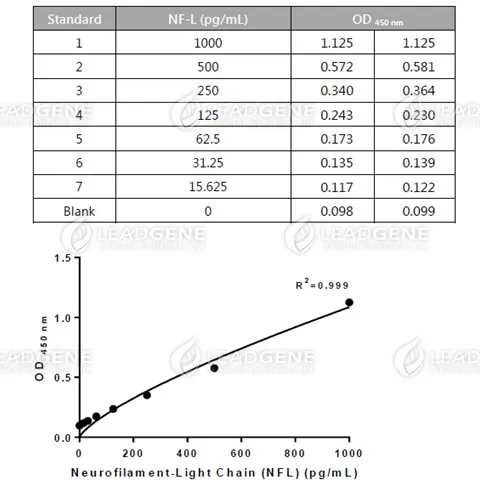
Description
Neurofilaments (NF) are assembled as heteropolymers, found exclusively in neurons, and serve as axonal scaffolding. They are composed of three subunits, including NF-L (68 kDa), NF-M (95 kDa), and NF-H (115 kDa), that are essential for axonal growth and maintenance. Elevated NF-L levels in serum and CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) have been correlated with axonal damage in Multiple Sclerosis patients, serving as a prognostic marker. In addition, plasma NF-L concentrations were highly significantly higher in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
Test Principle
Human NF-L ELISA kit is used to detect NF-L in samples by sandwich ELISA method. This assay uses microplate pre-coated with mouse anti-human NF-L monoclonal antibody to the solid phase. Human NF-L in the sample conjugates on solid phase and then react with the HRP conjugated mouse anti-human NF-L monoclonal antibody. Subsequent wash steps will remove residual unbound antibody. After incubation with substrate solution, the reaction is determined by the absorbance at 450 nm. Quantification of nuclease level is accomplished by comparing the absorbance with standard curve.